San Bernardino Water Quality at a Glance
multiple contaminants
Is San Bernardino Water Safe to Drink?
Meets Federal Standards, Some Concerns Remain – San Bernardino water complies with federal standards but contains multiple contaminants including arsenic, chromium-6, and disinfection byproducts. The city draws from the Bunker Hill Basin aquifer and imports State Water Project water. Key concerns include trihalomethanes (cancer-causing disinfection byproducts), naturally occurring arsenic, and chromium-6. The Newmark Groundwater Contamination site affects parts of the region with volatile organic compounds.
⚠️ Key Concerns for San Bernardino Residents
- Disinfection Byproducts: Trihalomethanes (THMs) including chloroform, bromodichloromethane, and bromoform detected; formed during chlorine treatment
- Heavy Metals: Arsenic and chromium-6 (hexavalent chromium) present at levels exceeding health guidelines; both are known carcinogens
- Groundwater Contamination: Newmark site affects 8-square-mile area with volatile organic compounds including PCE and TCE
- Mixed Water Sources: Combination of local groundwater and imported State Water Project water; quality varies by source and season
Read the full report below for detailed analysis, city-specific data, and actionable recommendations for San Bernardino residents.
San Bernardino – California – Water Quality Report 2025: PFAS Testing, Infrastructure Concerns & Safety across your city
San Bernardino Municipal Water Department provides comprehensive water services to approximately 216,000 residents across the City of San Bernardino and surrounding areas. Established as a municipal utility in 1905, the system delivers water through its service area, making it one of the oldest municipal water departments in California.
San Bernardino sources its drinking water primarily from the Bunker Hill Groundwater Basin, located in the northwestern portion of the city, with water naturally replenished by rain and snowmelt filtering through the San Bernardino Mountains. This local groundwater source is shared with over 20 other local public and private water suppliers. The utility also imports water from California’s State Water Project to supplement local supplies and recharge groundwater basins. San Bernardino’s water meets federal and state quality standards, with treatment technologies including advanced filtration systems.

San Bernardino Water Quality: Current Status (2024-2025)
Latest Testing Results
- EPA Compliance: For the latest quarter assessed by the U.S. EPA (April 2024 – June 2024), San Bernardino’s tap water was in compliance with federal health-based drinking water standards, though meeting federal standards does not guarantee the water meets the latest health guidelines.
- Testing Scope: The Water Quality Control section conducts comprehensive water quality monitoring throughout the distribution system, adhering to monitoring schedules established by state and federal agencies.
- Contaminant Detection: Independent testing has found multiple contaminants including arsenic, chromium-6, trihalomethanes, and various disinfection byproducts, though levels remain within federal legal limits.
Water Sources
- Bunker Hill Groundwater Basin: Primary source located in the northwestern portion of the city, shared with over 20 other local public and private water suppliers serving the greater region.
- State Water Project: Supplemental imported water from Northern California helps replenish local groundwater basins and provides system reliability during drought conditions.
- Watershed Protection: Natural recharge from rain and snowmelt filtering through the San Bernardino Mountains, with regional watershed protection plans.
Advanced Treatment Technology
- Water Treatment Systems: San Bernardino employs treatment systems designed to address various contaminants, including filtration and disinfection processes to meet regulatory standards.
- Contaminant Management: The Newmark Groundwater Contamination site in San Bernardino is addressed through federal, state and municipal actions, with three groundwater treatment plants constructed to manage an 8-square-mile area of contamination.
- Disinfection Systems: Chlorine disinfection is used throughout the distribution system, though this process creates disinfection byproducts including trihalomethanes that have been detected in the water supply.
Infrastructure Modernization
- Distribution System: Water distributed through multiple pressure zones with reservoirs providing storage capacity throughout the San Bernardino service area.
- Regional Coordination: San Bernardino participates in regional water supply planning and coordinates with neighboring utilities for water resource management and emergency response.
- Ongoing Improvements: The utility continues to invest in infrastructure modernization and treatment technologies to address emerging contaminants and maintain compliance with evolving regulations.
Customer Protection Initiatives
San Bernardino Municipal Water Department provides customer support through water conservation programs and maintains a Cross-Connection Control Program to protect the public water supply from contamination. The utility offers customer service available 24/7 at 909-384-5095. Educational outreach helps residents understand water quality and conservation practices. San Bernardino’s commitment to water quality includes communication through annual Consumer Confidence Reports and ongoing investments in treatment technologies and infrastructure to ensure safe drinking water that meets all regulatory requirements.
Recommendations for San Bernardino Residents
Test Your Water
Request water quality information from San Bernardino Municipal Water Department by calling 909-384-5095 or reviewing their Consumer Confidence Reports online. Independent water testing may be beneficial given the detection of multiple contaminants including arsenic, chromium-6, and disinfection byproducts.

Maximize Conservation Rebates
Take advantage of San Bernardino’s water conservation rebate programs for water efficiency upgrades. Contact the utility for current rebate offerings on high-efficiency appliances, fixtures, and landscaping improvements.
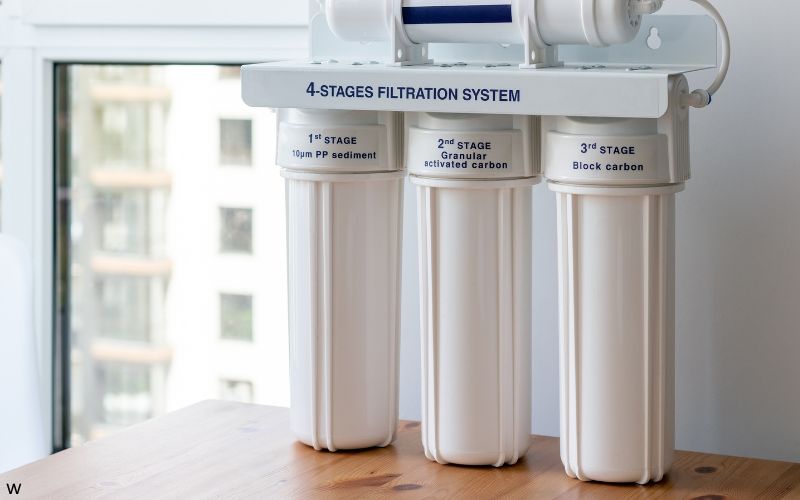

Consider Home Filtration
Given the presence of arsenic, chromium-6, trihalomethanes, and other detected contaminants, residents may benefit from NSF-certified filters designed to remove these specific contaminants, particularly for drinking and cooking water.

Follow Water Efficiency Standards
Comply with San Bernardino’s current water use efficiency standards: irrigate only during permitted hours and days. Help protect local water supplies by avoiding water waste and embracing conservation practices.

Report Issues
Contact San Bernardino Municipal Water Department Customer Service at 909-384-5095 (available 24/7) for water main breaks, pressure problems, or quality concerns. Prompt reporting helps maintain system integrity and water conservation efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is San Bernardino’s tap water safe to drink?
San Bernardino’s tap water meets federal and state drinking water standards. The city’s water comes primarily from the Bunker Hill Groundwater Basin, which is naturally replenished by rain and snowmelt from the San Bernardino Mountains.
However, independent testing has detected multiple contaminants including arsenic, chromium-6, and trihalomethanes. While these levels remain within federal legal limits, they may exceed health guidelines established by environmental health organizations. San Bernardino Municipal Water Department conducts water quality monitoring using treatment systems designed to address various contaminants. Annual Consumer Confidence Reports provide transparency about water quality testing results.
Why might my water taste or smell different sometimes?
Occasional taste and odor changes can occur due to several factors:
1. Seasonal variations: Natural changes in groundwater quality can occur during heavy rainfall or drought periods
2. Treatment processes: Chlorine disinfection used throughout the system may cause taste variations and creates disinfection byproducts
3. Home plumbing: Internal plumbing issues or infrequently used faucets can sometimes cause taste or odor concerns
If taste or odor issues persist, contact San Bernardino Municipal Water Department at 909-384-5095 for assistance. Running cold water for a few minutes after periods of non-use can often help improve water quality from your tap.
Does San Bernardino have lead in its water system?
According to available data, San Bernardino’s water system has maintained compliance with federal lead and copper regulations:
• Current status: Testing shows lead levels well below federal action limits, though legal limits for contaminants have not been updated in almost 20 years
• Treatment approach: The utility uses treatment technologies and monitoring to address potential lead issues in the distribution system
• Source quality: The Bunker Hill Groundwater Basin provides the primary water source with natural filtration through mountain aquifers
• Ongoing monitoring: Regular testing is conducted throughout the distribution system with results reported annually
Homes built before 1986 may have lead components in internal plumbing. Contact San Bernardino Municipal Water Department at 909-384-5095 if you have concerns about your home’s plumbing system.
Are there water restrictions in San Bernardino?
San Bernardino operates under water use efficiency standards as part of ongoing water management efforts:
Current Water Use Standards:
• Irrigation timing restrictions to maximize water efficiency
• Compliance with state requirements to avoid wasteful water practices
• Participation in regional water conservation initiatives
Conservation Requirements:
San Bernardino is subject to state conservation regulations requiring urban water suppliers to meet water budgets to ensure sustainable water supplies for the future.
Current conservation programs and restrictions are available at sbmwd.org or by calling 909-384-5095.
Quality News About Your Water
Get the comprehensive water quality news coverage you need with our dedicated US Water News Service. From coast to coast, we deliver in-depth reporting and expert analysis on PFAS contamination, EPA regulatory changes, infrastructure developments, and emerging water safety issues affecting communities nationwide. While mainstream media only covers the biggest stories, we provide the detailed, ongoing coverage that helps you understand the full scope of America’s water challenges. Whether you’re a concerned citizen, water professional, or community leader, our daily updates and analytical insights keep you informed about the issues that matter most to public health and environmental safety.
Contaminants of Concern

Volatile Organic Compounds
Source: The Newmark Groundwater Contamination site affects an 8-square-mile area in San Bernardino with volatile organic compounds including tetrachloroethylene (PCE) and trichloroethylene (TCE) from industrial activities
Health Effects: Various health concerns depending on specific compounds, including potential impacts on liver, kidney, and nervous system function
Current Status: Three groundwater treatment plants have been constructed to address the contamination, with ongoing operation, maintenance activities and monitoring EPA Limits: Various maximum contaminant levels depending on specific compounds

PFAS Compounds
Source: Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances from industrial activities, firefighting foams, and consumer products that can enter groundwater systems. San Bernardino County wells tested in 2019 showed levels below reportable thresholds for PFOA and PFOS
Health Effects: Research suggests potential concerns including impacts on immune system, thyroid function, cholesterol levels, and possible links to certain cancers
Current Status: California has expanded PFAS testing in drinking water supplies statewide, with San Bernardino monitoring developments in treatment technologies and regulatory requirements EPA Limits: New federal regulations for specific PFAS compounds were finalized in 2024
Please read – our information
The information presented on cleanairandwater.net is compiled from official water quality reports, trusted news sources, government websites, and public health resources. While we strive for accuracy and thoroughness in our presentations, we are not scientists, engineers, or qualified water quality professionals.
Our mission is to present water quality information in an accessible, real-world format that helps people understand what’s in their water and make informed decisions about their health and safety. We believe that complex environmental information should be available to everyone in a format that’s easy to understand.
We make every effort to ensure our content is current and accurate, but we cannot guarantee that all information is complete or error-free. This website should not replace official communications from your local water utility or health department. We always recommend consulting official sources for the most up-to-date information regarding your specific water system.
Clean Air and Water is not liable for any unintentional errors, omissions, or outdated information. The content on this site is provided for informational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice.


